
Different types of arthritis exist, each with separate causes including wear and tear, infections, and underlying diseases. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory condition that can affect more than just joints.
The main difference between osteoarthritis and RA is the cause behind the joint symptoms. Osteoarthritis is caused by mechanical wear and tear on the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s own immune system attacks the body’s joints and tissue.
RA mainly attacks the joints, usually many joints at once. RA commonly affects joints in the hands, wrists, and knees. In a joint with RA, the joint lining becomes inflamed, causing damage to joint tissue. This tissue damage can cause long-lasting or chronic pain, unsteadiness, and deformity. RA can also affect other tissues throughout the body and cause problems in organs such as the lungs, heart, and eyes.
There is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis. The treatment goal is to prevent joint damage, deformity, and disability.
When a patient reports a history of rheumatoid arthritis, the physician or other healthcare provider must validate this diagnosis through review of prior medical records, diagnostic test results, and consulting specialist reports.
Do not document rheumatoid arthritis as a confirmed condition if it is only suspected and not confirmed. Rather, document signs and symptoms in the absence of a confirmed diagnosis.
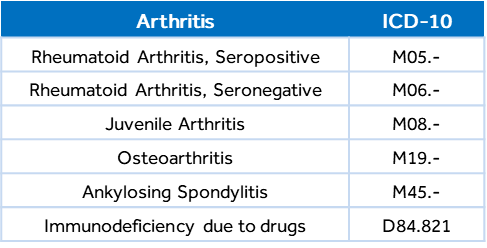
Immunosuppressant drugs are commonly used in the treatment of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis for the express purpose of suppressing the immune system. Assign code D84.821, Immunodeficiency due to drugs.
Documentation & Coding
Etiology of arthritis is critical to document. The default for arthritis not further specified codes to unspecified osteoarthritis, unspecified site. Be sure to include the following in your documentation:
- Type of arthritis
- Laterality and joints affected
- Treatment and medications
- Diagnostic findings such as imaging or labs
- Signs and symptoms
- Objective findings such as nodules
To ensure accurate, complete, and specific diagnosis code assignment, the coder must review the entire medical record and note the exact rheumatoid arthritis description documented during the visit.
SOURCES: FY24 ICD-10 Guidelines; Arthritis Foundation;

